ScienceInfoopk.com
ScienceInfopk
QUESTION 1
DESCRIBE MEDIAN NERVE ACCORDING TO THE FOLLOWING
A ) ORIGIN
B) ROUTE VALUE
C) RELATIONS
QUESTION 2
DESCRIBE THE CLINICAL IMPORTANCE OF MEDIAN NERVE.
QUESTION 3
HOW MEDIAN NERVE ENTER AND LEAVE FORE ARM.
QUESTION 4
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN
1. high median nerve palsy
2.low median nerve pasy
QUESTION 5
EXPLAIN THE FOLLOWING
1) PHALEN’S MANEUVER
2) TINEL’S SIGN
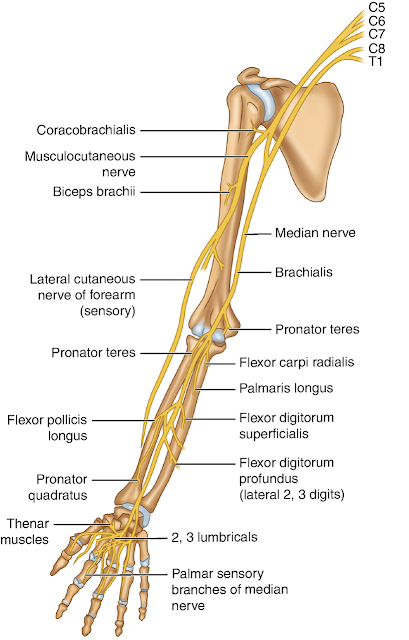
MEDIAN NERVE ANATOMY
Root value:
C5, 6, 7,8 and T1 As it runs in the
median plane of the forearm, so its
called median nerve. > it arises in the
axilla by 2 roots 1) Lateral (from lateral cord of brachial plexus) 2)
Medial root (from the medial cord of
the brachial plexus) .
IN AXILLA
Median nerve is formed by lateral
root from lateral cord and medial root
from medial cord of brachial plexus.
Median nerve runs lateral to axillary artery.
IN ARM
Median nerve continues to run on the
lateral side of brachial artery till the
middle of arm, where it crosses infront
of the artery and passes anterior to the
elbow joint into forearm.
IN FOREARM
Median nerve enters to the forearm by
passing between two heads of pronator
teres,then deep to fibrous arch of
flexor digitorum superficialis,in
proximal third of fore arm.
In mid forearm, descends between
flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor digitorum profundus.
About 5cm above wrist, it comes to lie on the lateral side of the flexor
digitorum superficialis, becomes
superficial just above wrist.
IN HAND
Median nerve passes deep to the
flexor retinaculam and enters
the palm of hand.Here its muscular
branches supply muscles of thenar
eminence (abductor pollicis brevis,
opponens pollicis and flexor
pollicis brevis).
Finally it divides into 4 to 5 palmar digital branches
supplying lateral three and half digit and their nail
beds. Also, motor branches are given to the first and
second lumbrical muscles.
BRANCHES
In arm: vascular branches to the brachial(arm)
In forearm: muscular branches to all superficial
flexor muscles(pronator teres, flexor carpi
radialis, palmaris longus and flexor
digitorum superficialis).
Anterior interosseous:
which comes off the median nerve supplies lateral half of flexor digitorum
profundus, flexor pollicis longus and
pronator quadratus.
Articular branches :
supply the elbow joint and proximal ulnar joint.
Palmar cutaneous branch :
supply skin over thenar eminence andcentral part of palm.
Motor Functions.
The median nerve innervates the majority
of the muscles in the anterior forearm, and some intrinsic hand muscles.
IMPORTANCE OF MEDIAN NERVE :
Median nerve is most commonly injured
near the wrist or high up in the fore arm
AND CAUSE
1. high median nerve palsy
2.low median nerve pasy
1 LOW MEDIAN NERVE PALSY:
Injury in the distal third of the forearm
Cuts infront of wrist or by carpal dislocation.
There will be sparing of the forearm
muscles, but the muscles of the hand will
be paralysed.
Thenar eminence is wasted and thumb
abduction and opposition are
weak,Sensation is lost over the radial and
half digits and changes may be seen.
2 HIGH MEDIAN NERVE PALSY:
Injury proximal to the elbow generally due to forearm features or elbow
dislocation trauma may damage the nerve
at any level.
This will cause paralysis of all the muscles supplied by the median nerve in the forearm and hand.
FLEXOR POLLIS LONGUS :
This muscle is tested by holding
thumb at its base and patient asked to
bend the terminal phalanx
FLEXOR DIGITORUM SUPERFICIALIS AND
PROFUNDUS :
When the patient is asked to clasp the hands the index finger of
affected side fail to
reflex.
FLEXOR CARPI RADIALIS :
The hand deviates to ulnar side when it is flexed against resistance.
ABDUCTOR POLLICIS BREVIS :
The patient is asked to lay his hand flat on
the table, a pen is held above the palm and
the patient is asked to touch the pen with
his thumb(Pen test).
OPPONENS POLLICIS
Bring the tip of the thumb towards the tipsof other fingers. CLANICALS
PHALEN’S MANEUVER :
1. Diagnostic test for carpal tunnel syndrome
(inverse praying position to achieve maximal wrist flexion).
2. A person holds his or her forearms horizontally
and then pushes backs of the hands together
TINEL’S SIGN
Tinel's sign is positive when lightly
banging (percussing) over the nerve
elicits a sensation of tingling, or 'pins
and needles in the distribution of the nerve.
DIRECT COMPRESSION OVER TRANSVERSE LIAGAMENT FOR 30 SECONDS.
Role of median nerve:
In forearm, median nerve directly
innervates muscles in the superficial and
intermediate layers,superficial
layer,Pronator teres, flexor carpi radialis
and palmaris longus.
INJURY TO THE MEDIAN NERVE:
MUSCLES ARE TESTED
CARPAL COMPRESSION TEST



0 comments:
Post a Comment